[Dev Catch Up # 77] - DeepSeek-V3.1, HTTP headers for API, Prompting 101, How Google Docs work, Hyperclay, doxx, rendergit, plutoprint - A py library for converting html to pdf, and much more!
Bringing devs up to speed on the latest dev news from the trends including, a bunch of exciting developments and articles
Welcome to the 77th edition of DevShorts, Dev Catch Up!
For those who joined recently or are reading Dev Catch Up for the first time, I write about developer stories and open source, partly based on my work and experience interacting with people all over the globe.
Thanks for reading Dev Shorts! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
Some recent issues from Dev Catch up:
Join 8000+ developers to hear stories from Open source and technology.
Must Read
DeepSeek AI has released DeepSeek-V3.1. It is a hybrid model that supports both thinking mode and non-thinking mode. It is now available on Hugging face. Check the Hugging face page for model weights and other details about the model.
HTTP headers are an important part of API. They handle caching, compression, security, and more. Using them right makes your API faster and safer. Check this post to learn the key headers every backend developer should know.
Google Docs lets many people edit the same file at once without breaking it. This post covers how it manages concurrency, latency, and conflicts. It also explains why it prefers operational transformation over simple locks or diffs. Check this post to understand how Google Docs handles real-time edits.
Prompting is more than writing instructions. It’s about giving models the right structure, context, and examples. In this Anthropic session, the team builds a prompt step by step for a real-world case, showing how to add context and output formatting for reliable results. Check this video for best practices in prompt engineering.
OSS Highlight of the Week
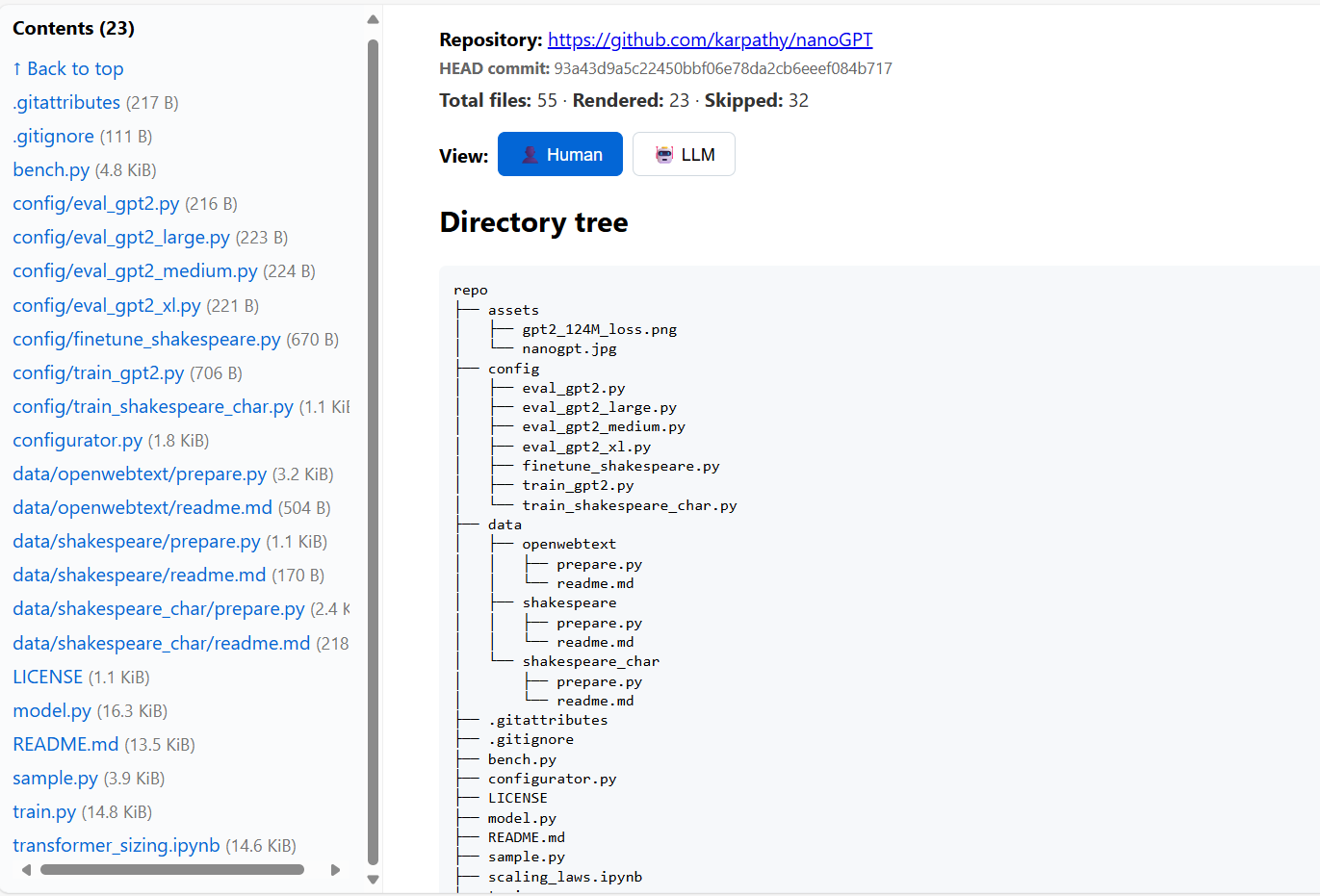
This week we are featuring rendergit, a tool that shows any GitHub repo as a single HTML page. It gives syntax highlighting, markdown rendering, and an option to copy the entire codebase for AI analysis. Perfect for quick code review or a fast Ctrl+F. Check the GitHub repo to try it out.
Good to know
Working with .docx files usually means opening Word. Doxx is a tool that lets you view them in the terminal, keeping tables and lists intact, with export to Markdown, CSV, or JSON. Check the GitHub repo if you want to handle word files from the command line.
If you are looking to learn about reinforcement learning, Unsloth has a clear guide. It explains RL with simple examples, covers methods like PPO, GRPO, and RLHF. It also has the video deep dive on RL, kernels, agents, and quantization. Check their docs for a quick start.
Many ML teams fail not because of models but because of architecture. Monolithic designs are easy to understand but don't use GPUs and CPUs well. Microservices, on the other hand, allow you to scale LLMs, RAG pipelines, and business logic independently. Check this post that explains the trade-offs for cost and speed.
xAI has released Grok 2 model weights on Hugging Face. It includes setup instructions for running the model. Check the repo if you want to try serving Grok 2 locally.
Notable FYIs
I have struggled to create PDFs with existing Python libraries, especially getting the style right. PlutoPrint makes it easier by turning HTML or XML into high-quality PDFs and images. Check the GitHub repo if you want a simple way to generate reports or invoices.
If you are a frontend developer check Hyperclay. It lets you edit a web page directly and saves the changes back into the HTML file. Check the Hyperclay docs to get started.
MIT’s new report shows only 5% of GenAI pilots drive revenue growth. The other 95% stall, not because of bad models but due to weak integration and workflow gaps. The study also found companies do better with vendor tools and partnerships than building on their own. Check the article if you find it interesting.
Most AI agents struggle with long-term memory. DiffMem tackles this by using Markdown for current state and Git history to track changes over time. Check the GitHub repo to explore this git-based memory system for AI.
That’s it from us with this edition. We hope you are going away with a ton of new information. Lastly, share this newsletter with your colleagues and pals if you find it valuable. A subscription to the newsletter will be awesome if you are reading it for the first time.