Most of us use AI agents every day. Many times, we do not even notice it. Agents are now common in coding, and they help us with many tasks.
We are now moving to the next stage of agent-based coding. We can use parallel agents to work on many features and fixes at the same time inside the same repo.
Claude Code and Cursor support parallel agents. They use Git work trees to give each agent its own space to work. You can follow the same approach by creating work trees in your project.
Let us first understand what Git worktrees are and how they help with parallel coding.
What is a Git worktree
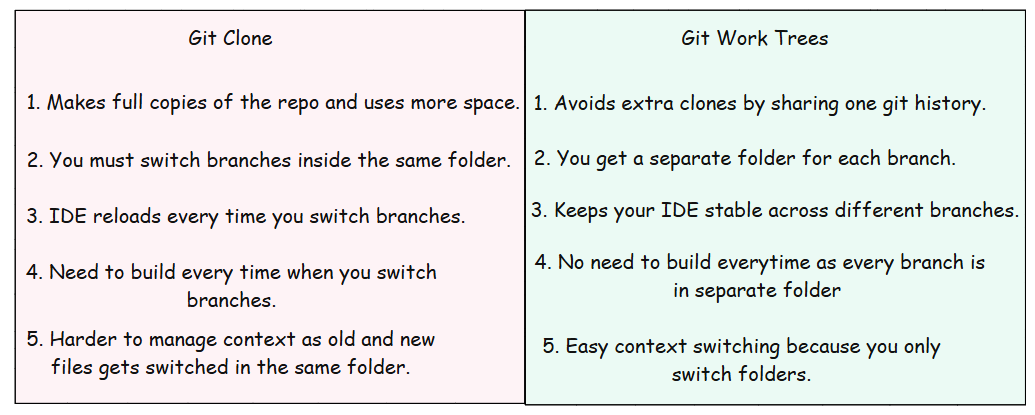
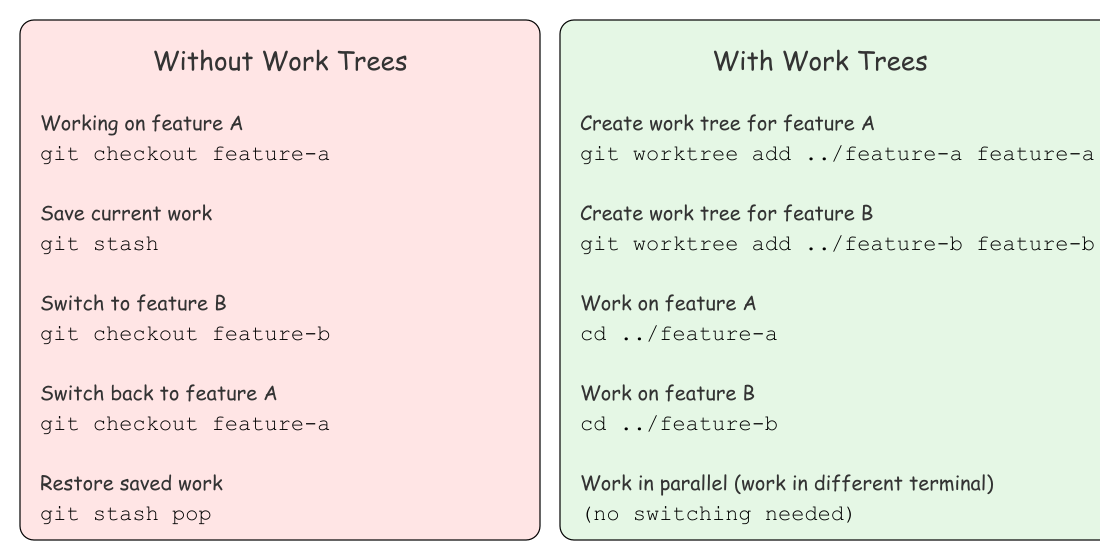
Git worktree Vs Git Clone
Git worktree Commands
Claude Code’s Parallel Agents with Git worktrees
Cursor’s Parallel Agents with Git worktrees
CodeRabbit’s Git worktree runner
1. What is a Git worktree
Git worktree is a feature in Git. Before we see Git worktree, let us see the normal Git flow.
The normal Git flow
You have one working folder.
You have one active branch.
Switching branches changes all files in that folder
my-app/
├── src/
├── README.md
└── .git/When you run git checkout “feature-abc”, the whole folder switches to that branch.
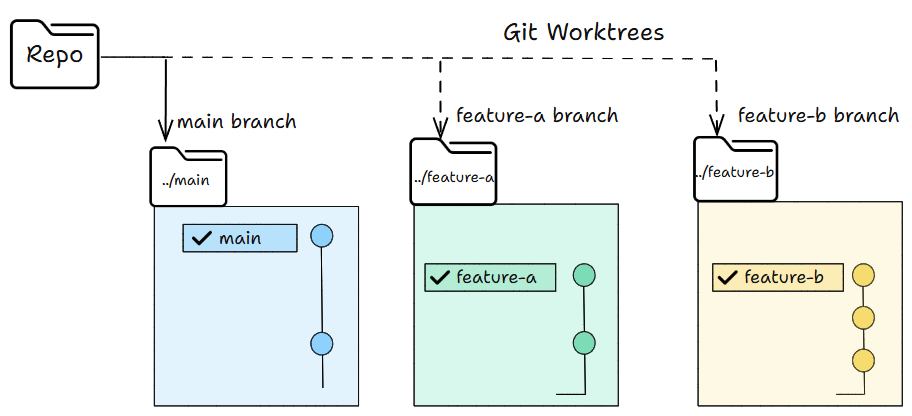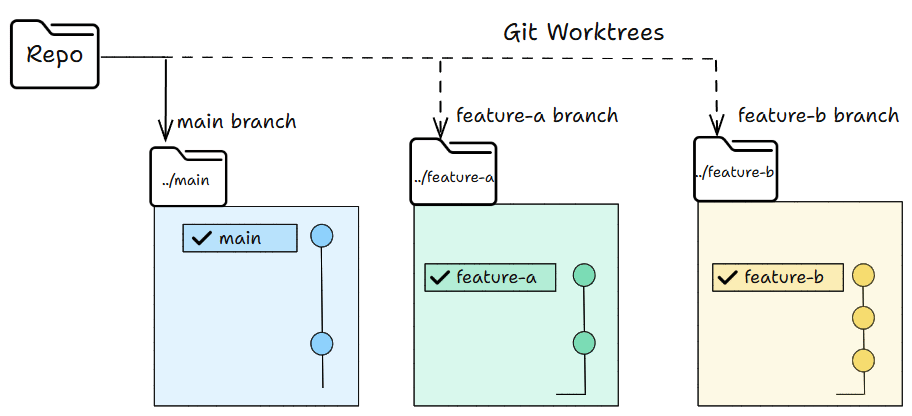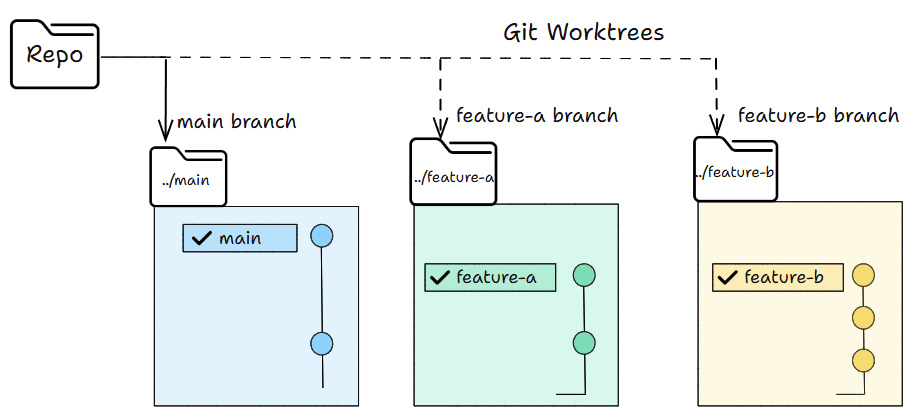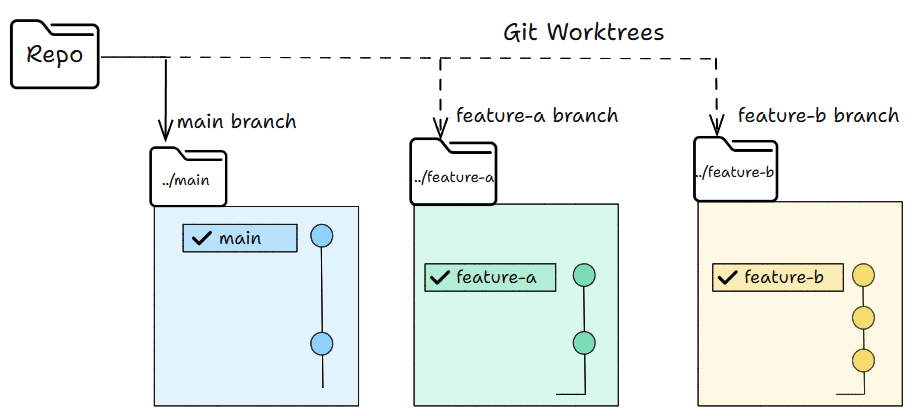
The Git work tree flow
Work trees let you have many working folders from the same repo.
Each folder can have its own branch.
You can work in all of them at the same time without switching anything.
In simple words, you can work in parallel without switching branches.
my-app/
├── src/
├── README.md
└── .git/
my-app-feature-a/ ← Worktree 1 (feature-a branch)
├── src/
├── README.md
└── .git ← File points to main repo
my-app-feature-b/ ← Worktree 2 (feature-b branch)
├── src/
├── README.md
└── .git ← File points to main repo2. Git worktree Vs Git Clone
The points above explain the concept. But the commands make it crystal clear.
This is what we do in a normal clone and what we do when we use work trees.
3. Git Worktree Commands
There are a few basic Git work tree commands you will use often.
1. Create worktree
# Create a work tree and a new branch
git worktree add <worktree-path> -b <new-branch-name>
# Example
git worktree add ../add-header -b feature/add-header
# Create a work tree from an existing branch
git worktree add <worktree-path> <branch-name>
# Example
git worktree add ../ui-changes feature/ui-changes2. List worktree
# list all active work trees
git worktree list3. Remove worktree
# remove a work tree
git worktree remove <worktree-path>
# Example
git worktree remove ../add-headerOne branch per Worktree Rule
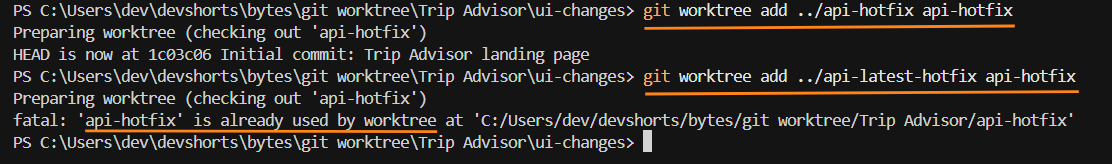
Git has a simple rule for work trees. One branch can live in only one work tree at a time.
If the branch is already used in a work tree, Git will block you from using it again. See the screenshot below.
4. Claude Code with Git worktrees
Claude Code can run parallel agents when you use Git work trees. Each work tree has its own folder and its own branch, so Claude can work on many tasks at the same time.
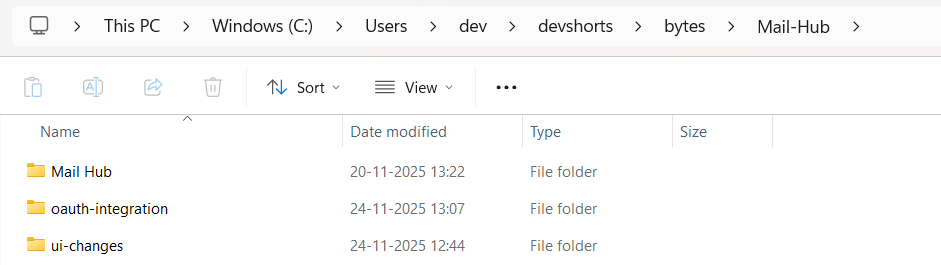
I was building a Gmail mail hub for my personal use. I had ui changes and oauth work going on at the same time.
Here is how I used Claude Code with work trees to build two features at the same time.
1. Created a new worktree for ui changes
git worktree add ../ui-changes -b feature/ui-changes2. Created another worktree for oauth integration
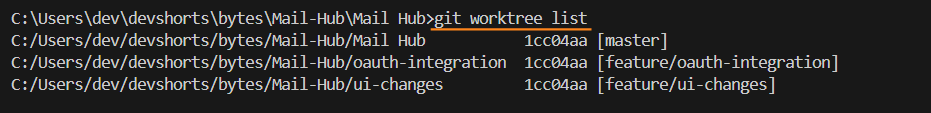
git worktree add ../oauth-integration -b feature/oauth-integrationAfter creating them, I listed the work trees to make sure everything was set:
You can also see the separate folders for each branch.
Now Claude Code can work across these branches without switching, as we have separate folders.
I worked on ui changes and oauth integration at the same time using Claude Code.
The video below shows how it works in real time.
5. Cursor’s Parallel Agents with Git Worktrees
Cursor makes it easy to run parallel agents by using Git work trees in the background.
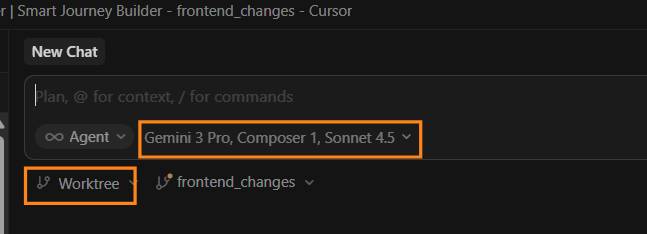
You can start by selecting a work tree and choosing many models for the same task, as shown in the image. Cursor will run the same prompt across all the selected models at once.
After you submit the prompt, Cursor shows one card for each model. You can click through the cards and see how each model changed the code.
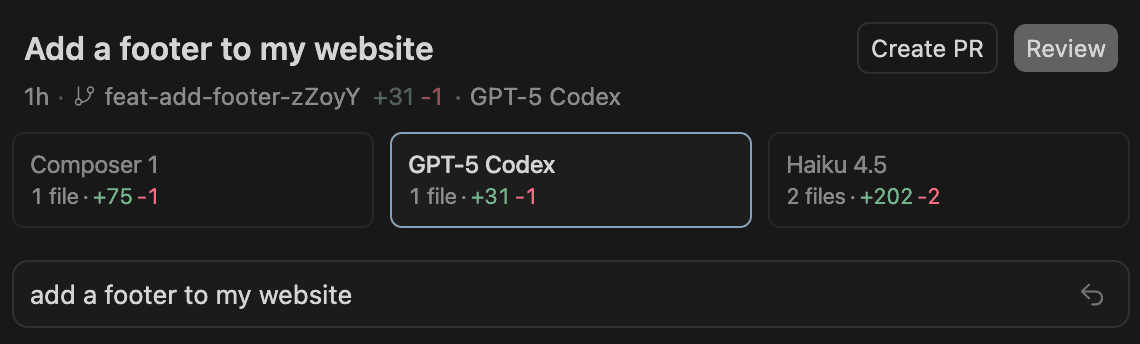
When you like one of the versions, you can click Apply. Cursor will bring those edits into your checked out branch.
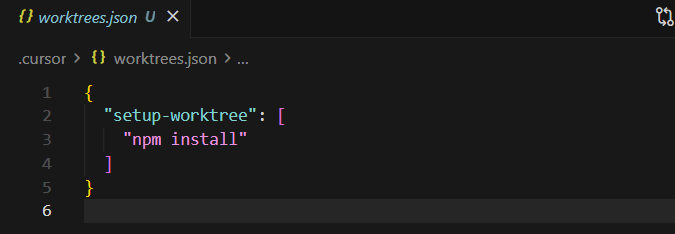
You can also customize worktrees by editing .cursor/worktrees.json file.
All commands you add under setup-worktree will run inside the work tree during setup.
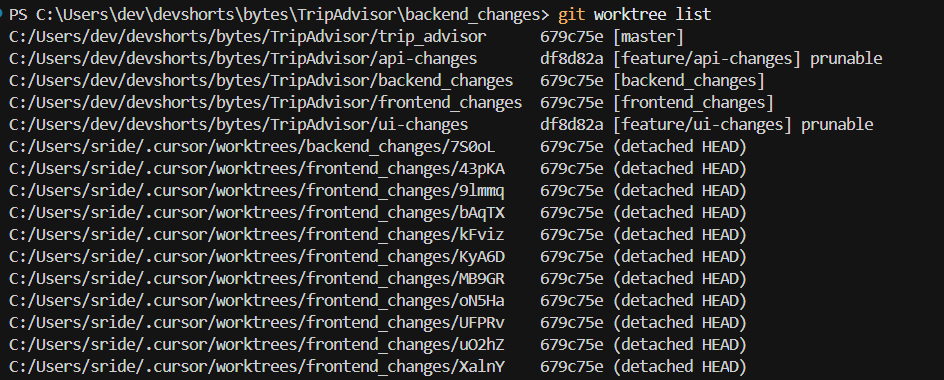
You can see all active worktrees anytime by running git worktree list. If you want to see Cursor created worktrees in your SCM panel, you can enable the git.showCursorWorktrees setting.
6. Git Worktree Runner - gtr
If you want a simpler way to handle worktrees, CodeRabbit offers a helper tool called Git Worktree Runner. It makes it easy to create, open, and manage worktrees with short commands. If you use worktrees often, this tool saves a lot of typing.
You can find it here: CodeRabbit’s Git Worktree Runner
Here is how you can install and use it.
# Installation
git clone https://github.com/coderabbitai/git-worktree-runner.git
cd git-worktree-runner
sudo ln -s “$(pwd)/bin/git-gtr” /usr/local/bin/git-gtr
# Usage
cd ~/your-repo # Navigate to git repo
git gtr config set gtr.editor.default cursor # One-time setup
git gtr config set gtr.ai.default claude # One-time setup
# Daily workflow
git gtr new my-feature # Create worktree
git gtr editor my-feature # Open in editor
git gtr ai my-feature # Start AI tool
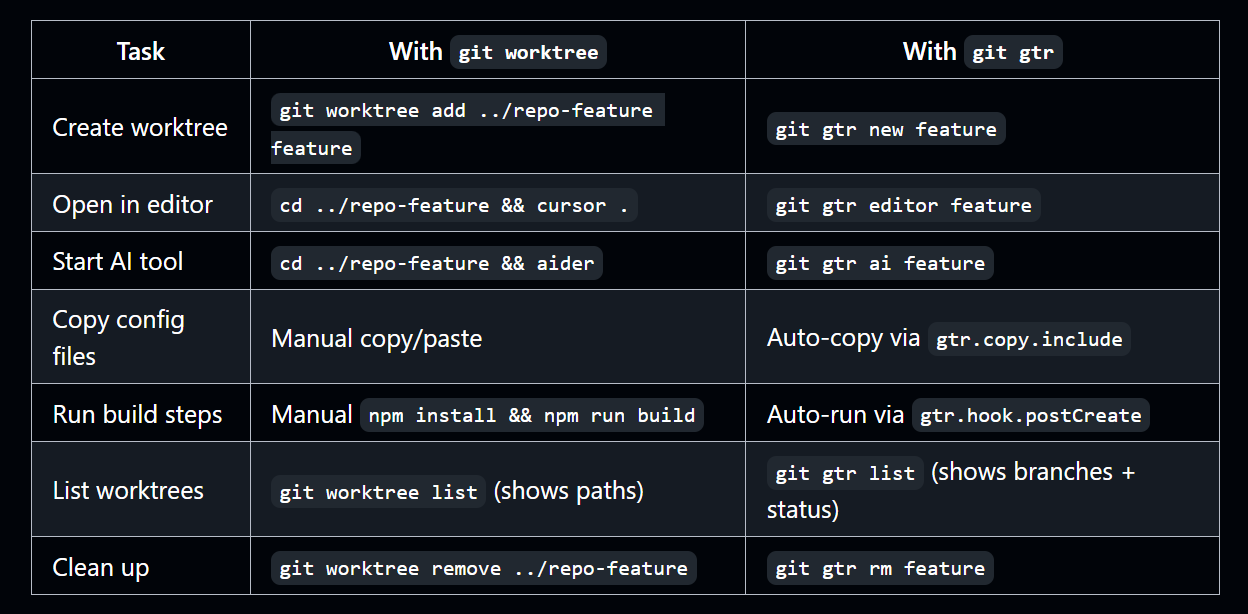
git gtr rm my-feature # Remove when doneThis table gives a quick comparison of Git worktree commands and the matching gtr commands.
Conclusion
We looked at Git worktrees and how they help with parallel agentic coding.
Worktrees let you build many features at the same time without switching branches or creating extra clones.
Tools like Claude Code, Cursor make it even better by linking every agent to its own work tree. This keeps your work clean, safe, and fast.
Once you start using work trees, it is hard to go back to the old single folder flow. You get more focus, more speed, and fewer mistakes with this new workflow. Try creating a few work trees for your next project and see how simple it feels to work on many features at the same time.
If you use any agent-based coding tool, work trees will become a natural part of your daily workflow.
Try now and let me know how it helps in your workflow!
Happy Learning!