AI agents are everywhere now. They are not just chatbots anymore. They are autonomous systems. They can reason, plan, and execute tasks without constant human oversight. Developers have started integrating them into real workflows.
I have written about agents before. Here are my blogs on them.
How to build a Full Stack Application using AI Agents
What are AI Agents and Must-Try Agents for Every Developer
Recently, OpenAI has shipped ChatGPT Agent. This can now do your work using its own computer. It can handle complex tasks from start to finish.
In this blog, we will cover ChatGPT Agent from features to architecture. Here is the outline.
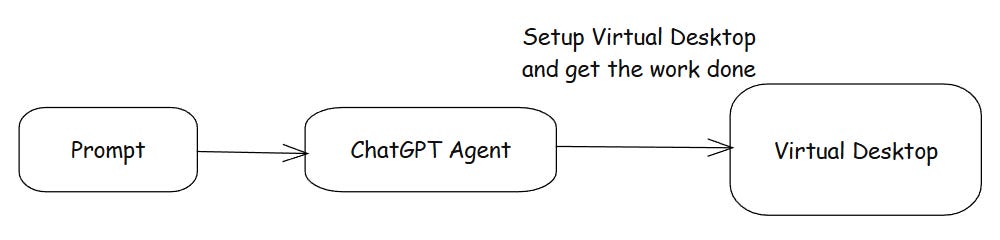
Browser Agent - ChatGPT Agent runs on its own virtual desktop.
Connectors - ChatGPT Agent uses Connectors to connect with external tools.
Scheduling - ChatGPT Agent has Scheduling option to schedule the task.
Website Permissions
How to allow ChatGPT Agent to access your website.
How to block the OpenAI crawlers accessing your site.
Architecture - ChatGPT Agent reverse engineered - live streaming & control
1. Browser Agent
Click Agent mode to activate ChatGPT Agent.
The ChatGPT Agent sets up its own virtual desktop and performs tasks. It can book tickets, create files, order items, or carry out any task based on the prompt.
It combines Operator mode and Deep Research. Operator could act. Deep Research could analyze. Now both run together in one unified flow.
It uses a browser agent that can browse and interact with websites. For sensitive actions like logins and credentials, it gives control back to user.
I tried ChatGPT Agent for a grocery order. The initial order was successful. On the second try it struggled because the item was out of stock, but overall, the experience was good.
The video below shows how it gives control back to users for sensitive steps like login.
The only drawback I noticed was that for a simple order it took quite a bit of time. If I had ordered, I would have done it faster. But I understand this is just the beginning, and the process will only get better over time.
2. Connectors
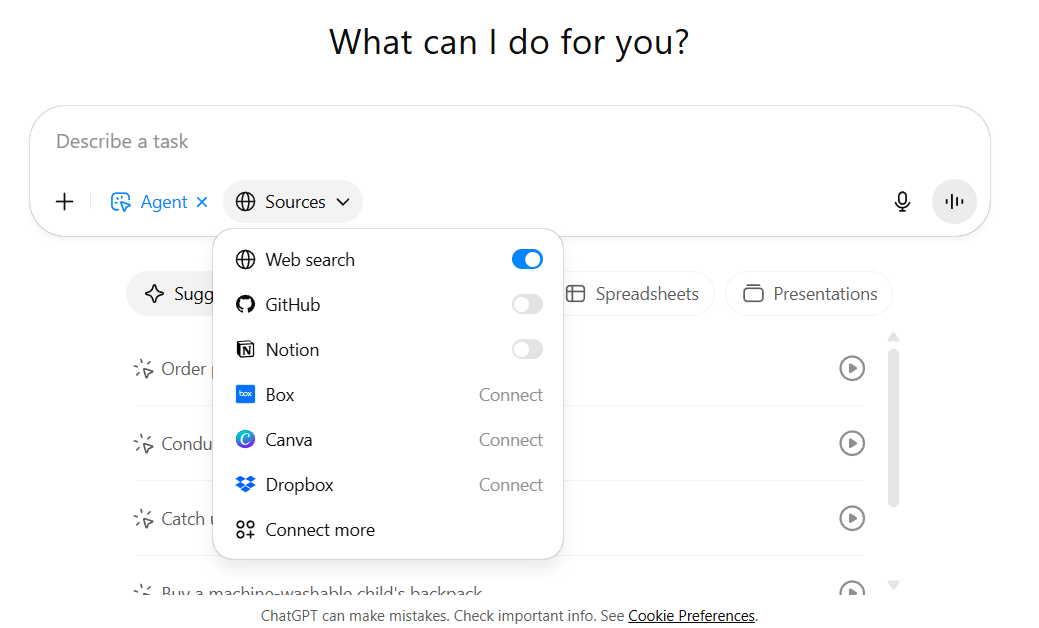
ChatGPT Agent can connect to external tools through connectors. Connectors have been in regular chat for a while. Now the Agent can use them too. And Web browsing is enabled by default for Agent.
You can find more connectors in Settings → Connectors.
When you connect a tool, you allow the Agent to read data and take actions in that tool. You still approve sensitive steps while it works.
You can add custom connectors too. They’re available for ChatGPT Pro, Team, and Enterprise workspaces. To create a connector, build an MCP server that links external tools or data sources, then deploy it, and connect it with ChatGPT.
If you want to learn more about MCP, check out my blogs on building MCP servers, deploying them, and adding OAuth support.
3. Scheduling
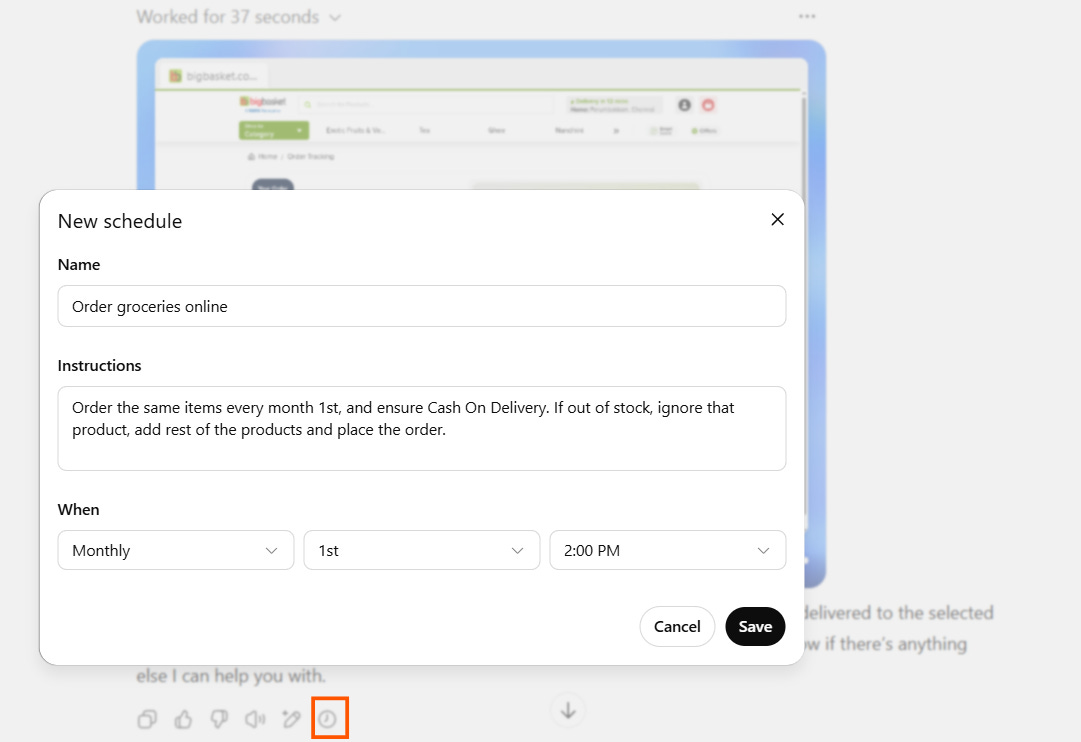
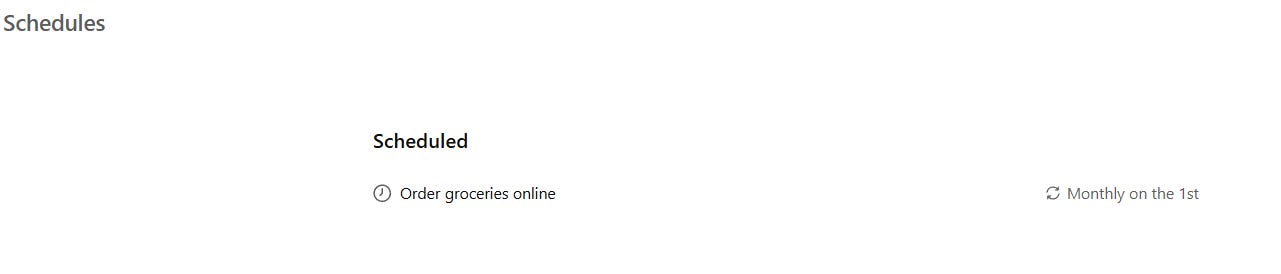
You can now schedule ChatGPT Agent tasks. For Example: Set up a monthly grocery order. Tell the Agent what to buy and set it to run every month. You can include instructions in the schedule. You can use the scheduling option for any kind of recurring tasks.
Manage the scheduled tasks under settings→ schedules.
4. Website controls
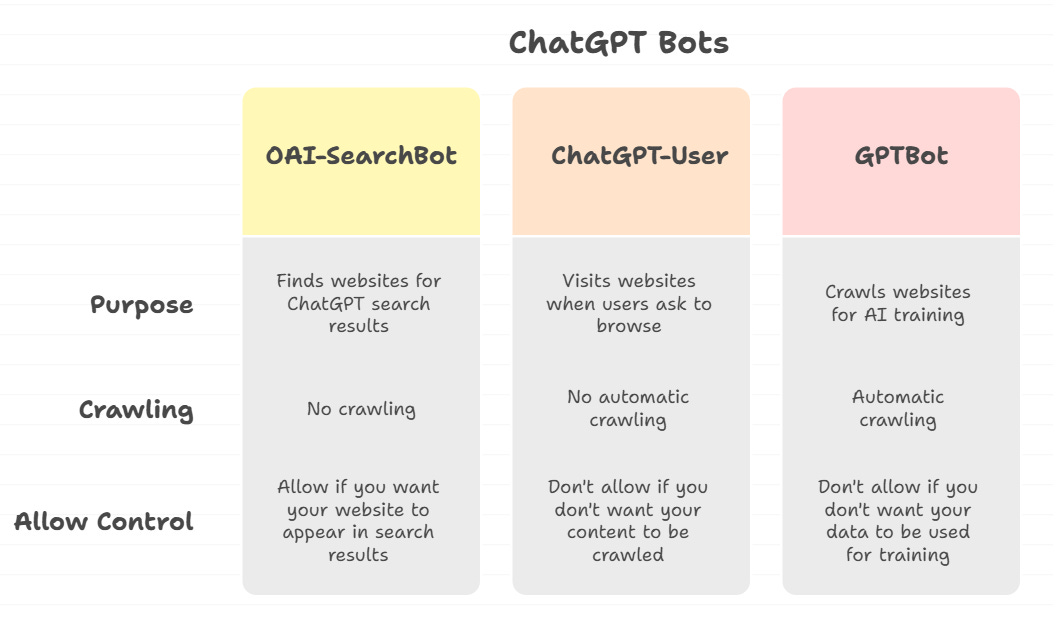
We all know ChatGPT access websites. OpenAI uses three types of crawlers for this. Each crawler is for different purposes. Website owners need to understand them. You can control which ones access your site.
How to block the ChatGPT bots
We listed the OpenAI bots above. To block them from your site, place the following entries in your robots.txt.
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Disallow: /
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /How to Allow ChatGPT Agent Access to Your Website
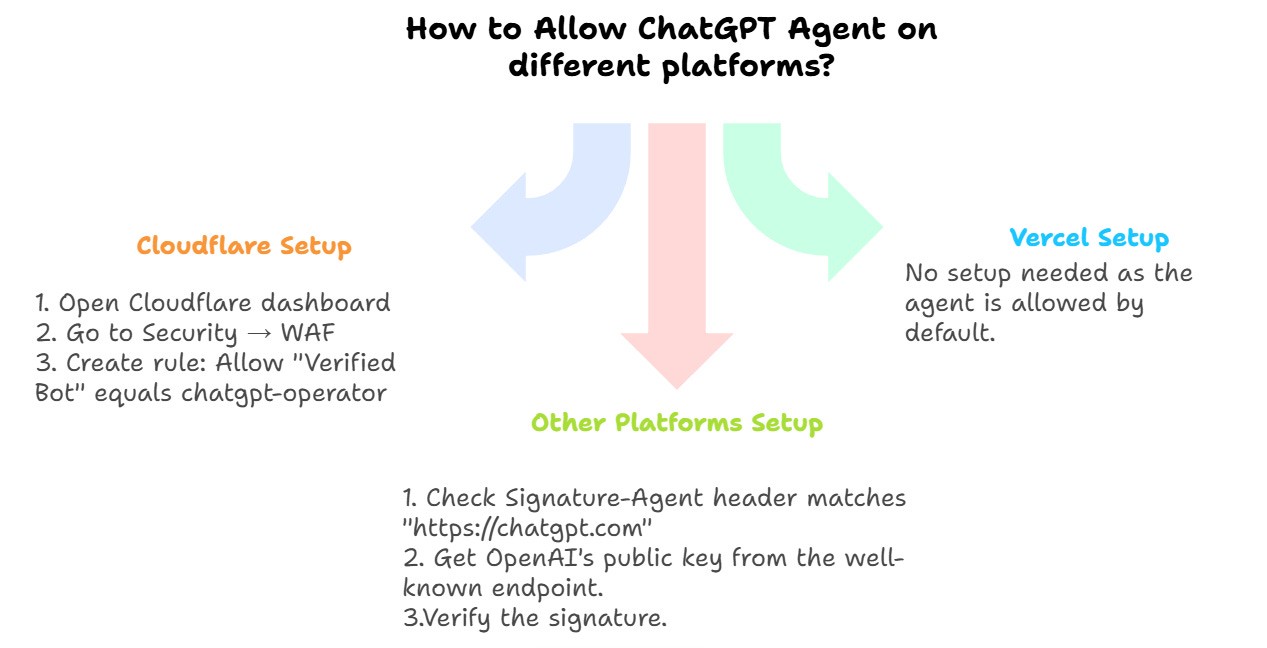
The ChatGPT Agent works like a bot that can perform real tasks on websites, from browsing pages to completing actions like shopping. Some site owners may want to allow the Agent to visit their site, since it handles genuine tasks like shopping or bookings.
The challenge is that fake bots could try to pretend to be ChatGPT Agent. To prevent this, you need a way to verify that a request is truly coming from the Agent.
OpenAI solves this by adding cryptographic signatures to every request. These signatures prove the request is genuine. By checking them, you can allow the real Agent while blocking impostors.
For detailed steps, see OpenAI’s guide on ChatGPT Agent allowlisting.
5. Reverse Engineering ChatGPT Agent
After looking at the features, I wanted to see how the Browser Agent actually works under the hood. Since its proprietary, the full architecture isn’t public. But I came across an article that reverse-engineered ChatGPT Agent and described a likely design.
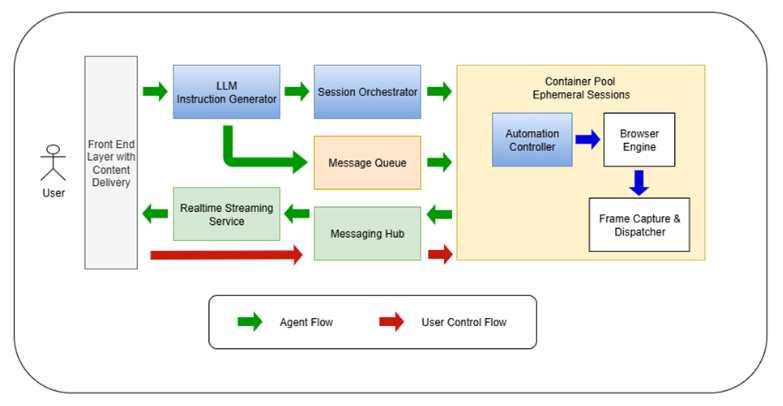
It explains how the agent launches a browser inside a virtual desktop, streams it live, and even hands control back to you when needed. When you move the cursor, those actions are applied directly to its virtual desktop. With the right workflow and infrastructure, this setup becomes possible.
A prototype built with this approach behaved much like ChatGPT Agent. You can see this prototype in action in the video below.
Source:- POC on ChatGPT Agent
To make it clearer, here’s a diagram showing steps of live streaming and user control.
Let us see the flow in detail now.
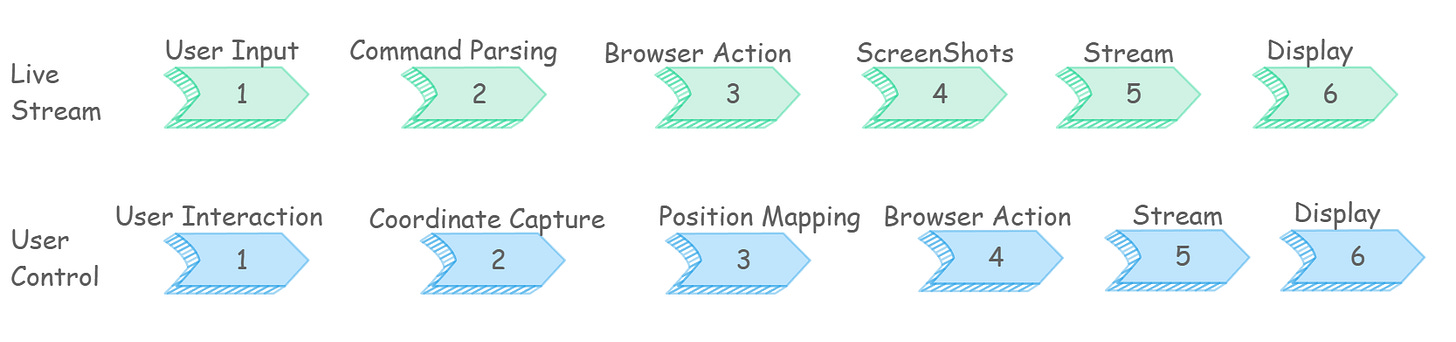
1. User Types Prompt in Chat Interface
The user enters a prompt in the chat. The system captures it and forwards it to the backend, where it’s added to a queue for execution.
2. Server Receives and Parses Command
The backend receives the request, analyzes the instruction, identifies the intended action, and extracts the key parameters needed to perform it.
3. Browser Action Execution
The backend sends the instruction to the browser session. The browser opens the target site, navigates to the right section, fills in fields, and performs the required clicks or actions.
4. Screenshot Capture and Processing
The system continuously captures snapshots of the browser at short intervals. Each snapshot is resized, compressed, and encoded so it can be streamed efficiently without losing clarity.
5. Real-Time Streaming and Display
The server streams the processed frames back to the client in real time. So, the user sees a smooth live view of the agent’s actions as they happen.
6. User Can Take Manual Control
When the user clicks on the live stream, the system captures the click coordinates and sends them to the backend. The virtual browser then performs the same action at that location.
7. State Synchronization and Maintains Session
The browser, backend, and client remain in sync so that actions and visuals stay aligned. If the connection drops, the session can recover without losing progress.
8. Continuous Feedback Loop
Every action is reflected in the next frame, creating a constant loop of feedback. The user gains confidence by seeing the process live and can choose to stop, take over, or let the Agent continue.
This is a likely architecture based on reverse engineering. It may not match the exact internal design of ChatGPT Agent, but a prototype built with this approach was tested and worked in a similar way.
Conclusion
Hope you now got a clear idea about ChatGPT Agent, its core features, and the architecture behind how it works.
For additional details about ChatGPT Agent, including how reinforcement learning guides tool selection, benchmark results, and safeguards against risks like prompt injection, check this video from OpenAI.
The agentic space is evolving fast, and we will see even more powerful agents as this technology matures.
Happy learning!